Running Artifactory 7 and Postgres using Docker Compose V2

When JFrog released Artifactory 7 they changed the way you can install Artifactory quiet a bit by introducing some sort of installation script for the Docker Compose setup. The documentation always was a bit brief and therefore I never understud why I need to download a TAR, then run a script on a server to get single instance of Artifactory up and running with Docker Compose.
Since then I always felt a bit lost, and honestly I did not want to spend time on investigating how the «new installation process» works and why I became more difficult. Starting in 2023 JFrog released this installation video that explains the simplest setup using Artifactory 7 with Postgres.
But again that video does helped me a lot, since I still need to run a script and that script produces two Docker Compose YAML files. One for Artifactory and another one for Postgres. That's not what I'm looking for. Furthermore, most or almost all examples related to Docker Compose refer to version 6 of Artifactory.
So this time I started digging. The intention of this blog post is to give experienced developers and/or ops a starting point. A Docker Compose YAML file that works, and simply can be developed further.
Let's start with the .env file that hold global configuration values. First of all we want to use Artifactory 7.55.9 which is the latest version as of this writing. With ROOT_DATA_DIR we set the root path for the Docker volumes (Postgres- & Artifactory data) to persist application data. Last but not least we define that port 8080 is the port Artifactory accepts external calls.
ARTIFACTORY_VERSION = 7.55.9
ROOT_DATA_DIR = /opt/jfrog/artifactory/volumes
JF_ROUTER_ENTRYPOINTS_EXTERNALPORT = 8080Then let's take a look at our docker-compose.yml. As mentioned before it contains a Postgres database «postgres» and Artifactory «artifactory».
version: '3.9'
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:13.9-alpine
container_name: postgresql
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=artifactory
- POSTGRES_USER=artifactory
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=gravis
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:5432:5432"
volumes:
- ${ROOT_DATA_DIR}/postgres/var/data/postgres/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
restart: always
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: "1.0"
memory: 500M
logging:
driver: json-file
options:
max-size: "50m"
max-file: "10"
ulimits:
nproc: 65535
nofile:
soft: 32000
hard: 40000
artifactory:
image: releases-docker.jfrog.io/jfrog/artifactory-oss:${ARTIFACTORY_VERSION}
container_name: artifactory
environment:
- JF_ROUTER_ENTRYPOINTS_EXTERNALPORT=${JF_ROUTER_ENTRYPOINTS_EXTERNALPORT}
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:${JF_ROUTER_ENTRYPOINTS_EXTERNALPORT}:${JF_ROUTER_ENTRYPOINTS_EXTERNALPORT}" # for router communication
# - 8081:8081 # for artifactory communication
volumes:
- ${ROOT_DATA_DIR}/artifactory/var:/var/opt/jfrog/artifactory
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
restart: always
logging:
driver: json-file
options:
max-size: "50m"
max-file: "10"
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: "2.0"
memory: 4G
ulimits:
nproc: 65535
nofile:
soft: 32000
hard: 40000
Additonally you need to configure Arifactory by providing a system.yaml configuration file.
shared:
node:
ip: 127.0.0.1
id: artifactory-one
name: artifactory-one
database:
type: postgresql
driver: org.postgresql.Driver
password: gravis
username: artifactory
url: jdbc:postgresql://postgres:5432/artifactory
router:
entrypoints:
externalPort: 8080
So this is how your directory should look like
.
├── .env
├── docker-compose.yml
└── volumes
└── artifactory
└── var
└── etc
└── system.yamlWhen running docker compose up -d and waiting while, you finally can login to your fresh Artifactory 7 installation on http://localhost:8080/ by using the default user admin with password password.
I hope this helps you setting up Artifactory. As mention this is the very minimum, feel free to extend it to your needs.
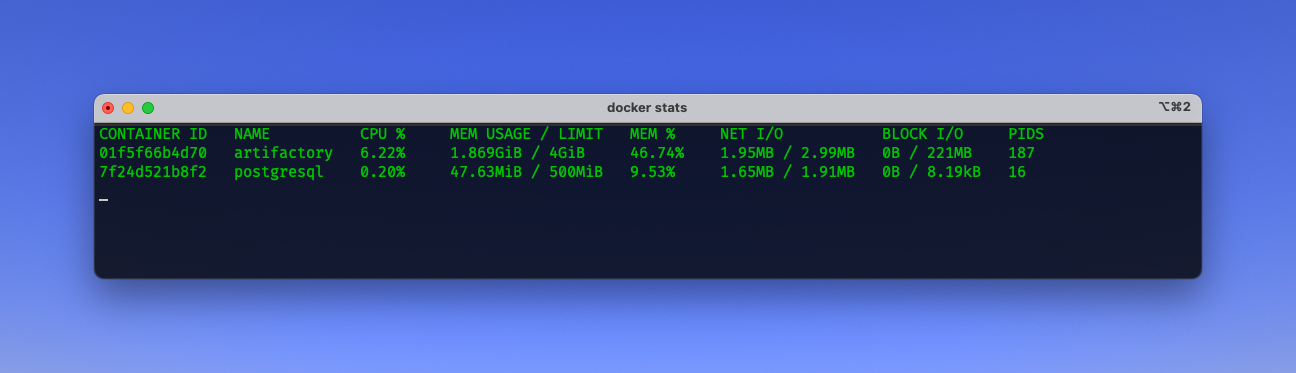
As a bonus please find the resource consumption of a bored Artifactory accompanied by a Postgres database running on Apple Silicon M1.